Raster Analysis Overview
GeoRetina AI offers a comprehensive suite of geospatial analysis capabilities, allowing you to extract valuable insights from both raster (satellite imagery) and vector data through a natural language interface.
Types of Analysis
GRAI supports two main categories of geospatial analysis:
Raster Analysis
Raster analysis involves working with satellite imagery and gridded data to analyze Earth's surface characteristics:
- Land Use/Land Cover Mapping: Classify surface types using AI models like Google Dynamic World.
- Urban Heat Island Analysis: Examine temperature variations across urban landscapes.
- LULC Change Detection: Track changes in land cover over time to identify trends.
- Vegetation monitoring (NDVI/EVI): Monitor vegetation health and growth patterns using Landsat and Sentinel-2 data.
- Weather forecasting: Access advanced weather predictions using Google DeepMind WeatherNext Graph dataset.
- Air Pollution Monitoring: Analyze patterns and trends in air quality indicators.
The Analysis Workflow
While each type of raster analysis has its specific parameters and outputs, all raster-based analyses in GRAI follow a similar workflow:
- Define your area of interest by drawing a region on the map
- Formulate your question in natural language (e.g., "Show me land cover types in this region")
- Refine parameters if prompted by the AI (time period, resolution, etc.)
- Interpret results displayed on the map and in the insights panel
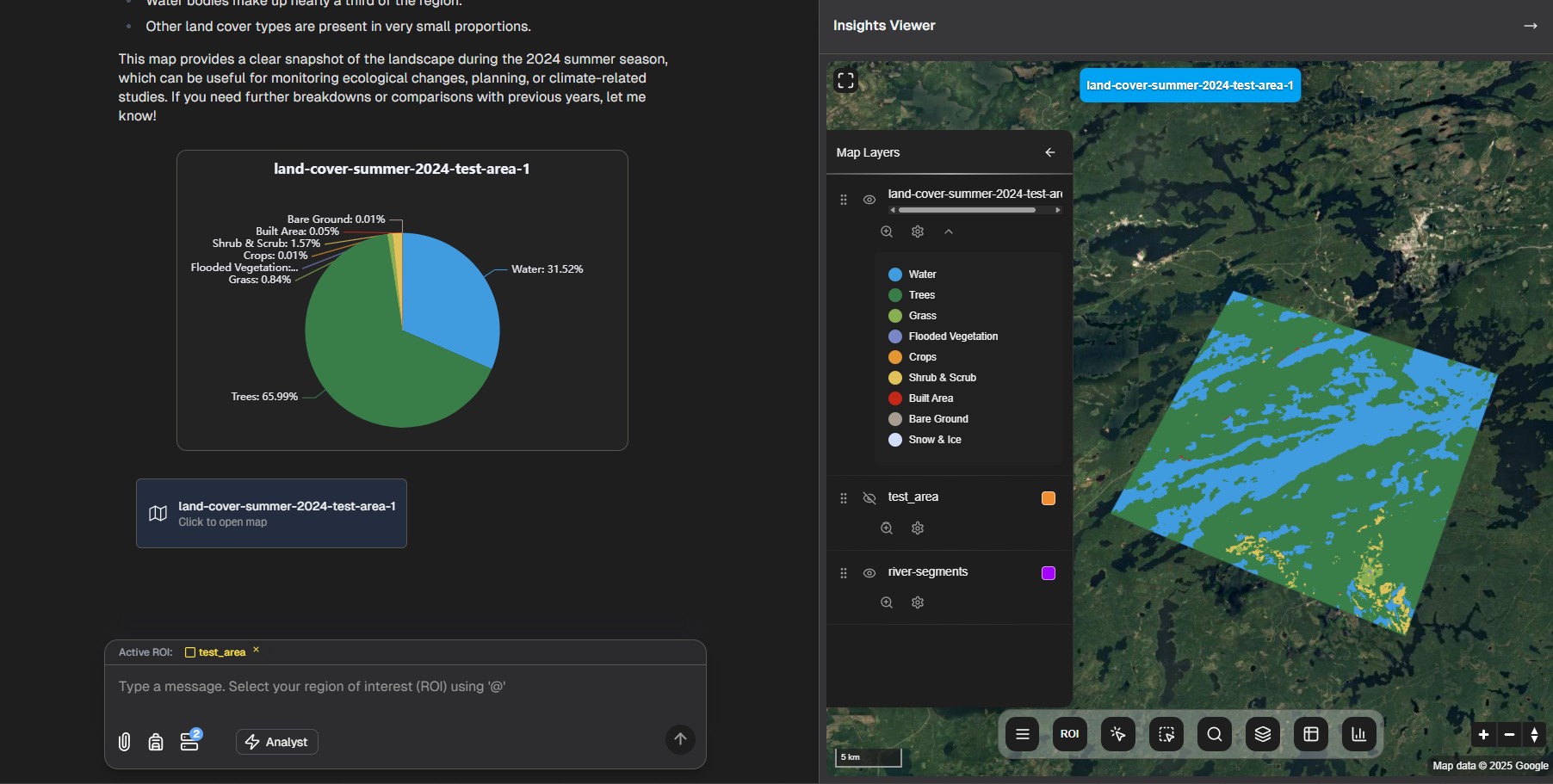
Example Applications
GRAI's geospatial analysis capabilities support various real-world applications:
Analysis Type | Applications |
|---|---|
| LULC Mapping | Urban planning, conservation monitoring, agricultural assessment, carbon stock assessment, ESG reporting |
| Urban Heat Islands | Public health, energy efficiency planning, urban development |
| LULC Change Detection | Environmental monitoring, compliance verification, disaster assessment, REDD+ monitoring, carbon offset verification |
| Vegetation Monitoring | Agricultural monitoring, forest health assessment, ecosystem management, biomass estimation, carbon sequestration monitoring |
| Weather Forecasting | Agricultural planning, event management, risk assessment, transportation |
| Air Pollution Analysis | Environmental health, policy development, urban air quality management |
Getting Started
To begin exploring geospatial analysis with GRAI:
- Follow the basic workflow guide to understand the interface
- Choose a specific analysis type from the navigation menu
- Experiment with different queries and parameters
- Combine different analyses to gain deeper insights
The following pages provide detailed instructions for specific types of analysis, starting with Land Use/Land Cover Mapping.